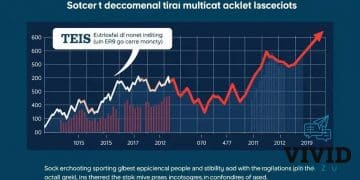
Flattened yield curve stokes investor concerns

A flattened yield curve indicates reduced differences between short-term and long-term interest rates, signaling economic caution and potential slowdowns, which impacts investor behavior and business investment strategies.
Flattened yield curve stokes investor concerns, suggesting uncertainties in the market. Have you noticed how this trend can affect your investments? Let’s dive into its implications.
Understanding the flattened yield curve
Understanding the flattened yield curve is crucial for investors. This economic indicator can reflect significant shifts in market sentiment. By analyzing it, investors can gain insights into potential future trends.
Defining the Flattened Yield Curve
A flattened yield curve occurs when the difference between short-term and long-term interest rates decreases. This condition signals various market behaviors and expectations. Often, it suggests that investors are anticipating slower economic growth.
Analyzing Its Implications
When the yield curve flattens, it’s essential to consider:
- The potential for an economic slowdown.
- Changing investor expectations regarding inflation.
- Policy shifts from central banks.
- Increased market volatility.
Investors carefully study these indicators to adjust their strategies. A flat curve often leads to hesitancy in long-term investments, as future returns become less certain.
Historical Context
Historically, flattened yield curves have preceded recessions. Understanding past instances helps investors recognize patterns and signals in the current market. For example, each time the yield curve has flattened substantially in recent years, it raised alarms about upcoming economic crises.
In summary, the flattened yield curve serves as an essential tool for investors to gauge economic conditions. By staying informed, they can make more strategic decisions regarding their portfolios. Recognizing this pattern and its implications can facilitate better investment choices and prepare for possible market changes.
What does a flattened yield curve indicate?
A flattened yield curve indicates significant shifts in market sentiment and can serve as an early warning sign for economists and investors. It often points to changing perceptions about future economic conditions.
Economic Slowdown Potential
One of the primary implications of a flattened yield curve is the expectation of slower economic growth. When the yield curve flattens, it suggests that short-term rates are high relative to long-term rates, indicating that investors might be cautious about future growth.
Investor Sentiment
Investors closely watch the yield curve because it reflects their sentiments about future interest rates and economic performance. A flat curve may lead to:
- Reduced investments in long-term projects.
- Increased demand for cash or cash-equivalents.
- Shifts in portfolio strategies to favor lower-risk assets.
- Concerns about inflation remaining subdued.
Such changes are driven by the belief that economic conditions are less favorable in the near future. This adjustment is crucial for managing risk within investment portfolios.
Central Bank Policy Impact
The flattening can also result from actions taken by central banks. When central banks raise short-term interest rates to combat inflation, long-term rates may remain stable or even decline. This situation fosters a flattening effect. Investors may then speculate about future monetary policy shifts that could impact various sectors of the economy.
In summary, a flattened yield curve signals caution among investors and can foreshadow economic changes. Recognizing these indicators helps in making informed decisions regarding investments and understanding broader economic trends.
Historical context of yield curves
The historical context of yield curves provides valuable insights into financial markets. Yield curves have been used as indicators to interpret economic conditions over time. Understanding their evolution helps investors navigate current trends.
Trends Over Time
Historically, yield curves have displayed different shapes, such as normal, inverted, and flattened. Each shape reflects distinct economic scenarios. A normal yield curve indicates growth, while an inverted curve often foreshadows recessions.
Economic Indicators
Different periods have shown how yield curves relate to economic events:
- In the 1980s, high inflation led to steep yield curves.
- The late 1990s showcased a flattening curve as the economy entered a growth phase.
- Post-2008 financial crisis, yield curves frequently flattened, suggesting market caution.
- The recent trend of low interest rates has also affected curve shapes.
These historical instances highlight the yield curve’s role in predicting economic shifts. Investors can analyze past data to recognize patterns that may influence future decisions.
Influences on Yield Curves
Several factors shaped historical yield curves, including monetary policy and global economic conditions. Central banks play a critical role in setting interest rates that impact short- and long-term yields. For example, aggressive rate cuts can lead to flattened curves, indicating market uncertainty. Comparatively, strong economic growth may result in normal curves as demand for credit rises.
In summary, the historical context of yield curves serves as a foundation for understanding current market dynamics. By looking back at how yield shapes have changed, investors can better anticipate future trends and make informed financial decisions.
Investor strategies in light of a flattened yield curve
Investor strategies in light of a flattened yield curve can significantly change. When faced with this market signal, investors need to adapt their approaches to navigate potential challenges.
Shifting Investment Focus
During periods of a flattened yield curve, investors often reassess their portfolios. This situation may lead them to:
- Increase their allocation in defensive stocks.
- Prioritize sectors less sensitive to economic downturns, such as utilities or consumer staples.
- Consider bonds with shorter maturities to reduce interest rate risk.
These sectors tend to perform better when economic uncertainty prevails. Investors want to ensure their assets are shielded from potential market volatility.
Exploring Alternative Investments
In addition to shifting focus within equities, some investors explore alternative investments. These may include:
- Real estate, which can provide consistent income.
- Commodities, serving as a hedge against inflation.
- Private equity, which might offer uncorrelated returns.
Such diversifications can help manage risk while pursuing potential gains during uncertain economic climates.
Overall, adapting investment strategies in response to a flattened yield curve is essential. By understanding the implications of this phenomenon, investors can position themselves to weather potential market storms and seize opportunities that arise during these periods of volatility.
Potential implications for the economy
The potential implications for the economy resulting from a flattened yield curve are significant and multifaceted. This financial signal can influence various aspects of economic activity, including consumer spending, business investment, and overall growth.
Consumer Behavior
When a yield curve flattens, consumer confidence may waver. Households often react by:
- Reducing spending due to concerns about future economic stability.
- Postponing major purchases, such as homes or cars.
- Saving more as a precaution against uncertain times.
This cautious behavior can dampen economic growth, as consumer spending is a major driver of the economy.
Business Investment Trends
Businesses also respond to a flattened yield curve. They might be more hesitant to invest in expansion or new projects. This reluctance can stem from:
- Uncertainty about the effectiveness of long-term investments.
- Potential risks associated with slowing economic conditions.
- Increased difficulty in securing financing at favorable rates.
As a result, capital expenditures may decline, impacting job creation and innovation.
Impact on Monetary Policy
A flattened yield curve can prompt central banks to reevaluate monetary policy. In response, they might:
- Consider lowering short-term interest rates to stimulate growth.
- Implement quantitative easing measures to encourage lending.
- Focus on communication strategies to build confidence among investors.
Such interventions aim to support economic stability during uncertain periods. Overall, the implications of a flattened yield curve can ripple through the economy, affecting everything from consumer confidence to central bank actions, thereby shaping the economic landscape.
In summary, a flattened yield curve is a crucial signal for both investors and the economy. It indicates cautious market sentiment and potential economic slowdowns. Understanding its implications helps investors adapt their strategies and manage risks effectively. By recognizing the signs that come with a flattened yield curve, individuals and businesses can prepare for what lies ahead. Staying informed about these changes contributes to more thoughtful decision-making in uncertain times.
FAQ – Understanding the Flattened Yield Curve
What is a flattened yield curve?
A flattened yield curve occurs when the difference between short-term and long-term interest rates decreases, often signaling economic uncertainty.
How does a flattened yield curve impact investors?
Investors may become more cautious, leading them to adjust their portfolios towards safer assets or defensive stocks.
What could a flattened yield curve mean for the economy?
It may indicate a potential slowdown in economic growth, affecting consumer spending and business investments.
How should businesses respond to a flattened yield curve?
Businesses may reconsider their expansion plans and focus on short-term financial stability while monitoring economic signals.